Atlas Agent
Background
Some features require Atlas Cloud to connect to your database. As it is uncommon for databases to be directly accessible from the internet, you can run Atlas Agents in your database's network to facilitate this communication. Agents register themselves via credentials against your Atlas Cloud account and continuously poll it for work.
The following features require an Atlas Agent installed in your databases network:
- Drift Detection
- Cloud mediated deployments (coming soon)
- Schema monitoring and auditing (coming soon)
Drift Detection is currently only available in a paid subscription.
Create an Agent
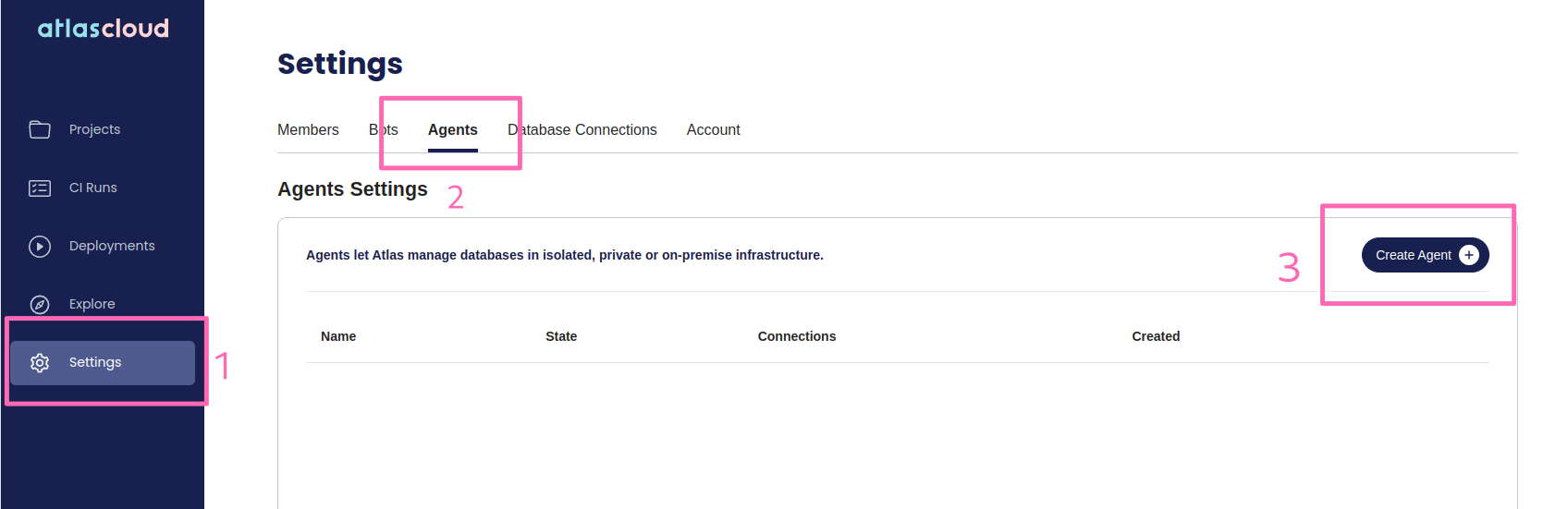
To create an Agent, head over to the general settings and click on the "Agents" tab.
Only admins can create Agents. Ensure you have sufficient permissions before proceeding.
Screenshot Example
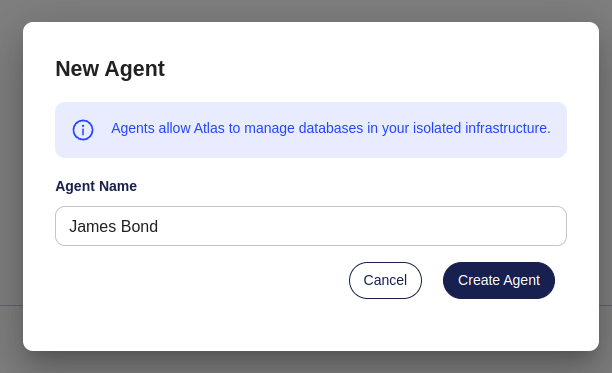
Pick a name for your Agent and hit Create Agent.
Screenshot Example
Connect the Agent
Now that we have created an Agent in your Atlas Cloud account, we can run an Agent process. This is typically done by running it in the same network as our target database. To authenticate against your Atlas Cloud account, a token will be created which you will need to provide the Agent with. Store this token in a secure place, as you won't be able to see it again. If needed, you can always create a new one later.
Screenshot Example
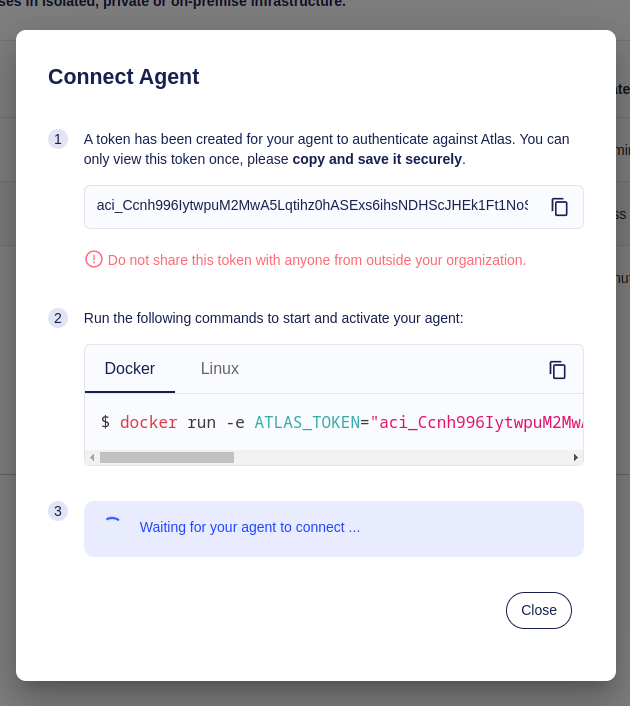
To start the Agent and let it poll work from Atlas Cloud, simply follow the instructions shown. Currently, Ariga provides two builds, a docker image and a linux amd64 binary. All you need to provide the Agent with is a token to authenticate against Atlas Cloud.
- Docker
- Linux
If you want to use the Docker image, run the following:
docker run -e ATLAS_TOKEN <your atlas token> arigaio/atlas-agent
If you want to use the linux build, run the following:
curl -L -o atlas-agent 'https://release.ariga.io/atlas-agent/atlas-agent-amd64-latest'
chmod +x atlas-agent
atlas-agent --token <your atlas token> arigaio/atlas-agent
If the Agent has access to the internet and can reach Atlas, you should see a success message.
Screenshot Example
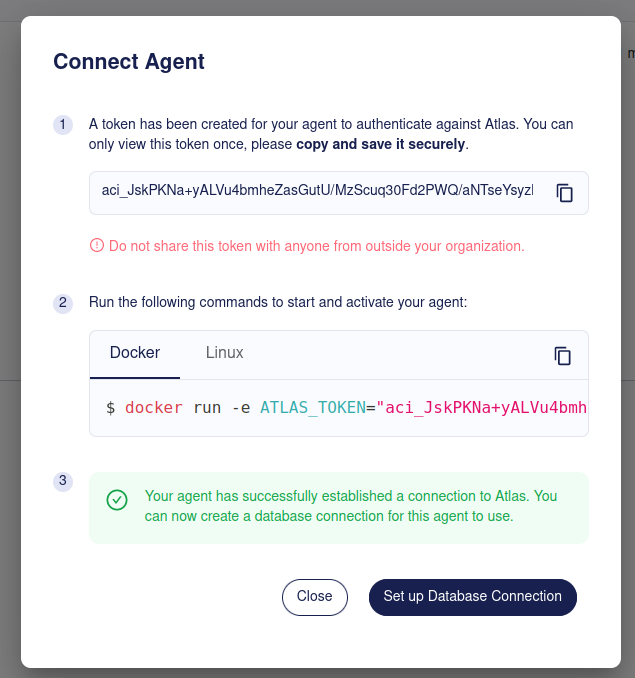
Now the Agent is running and can connect to Atlas. However, in order to connect to your databases, it needs to know how to obtain valid credentials and how to use them.
Database Credentials
Since we want the Agent to connect to our database on behalf of Atlas, it needs to know how to access it. For this we can assign an Agent multiple database connections. Either click the Set up Database Connection or select the Database Connections tab and hit Create Connection.
You can only create a connection with an actively running Agent. If there is no Agent selectable in the dropdown, ensure the Agent binary is still running and has access to the cloud.
Fill out the form with the connection details to your database.
Screenshot Example
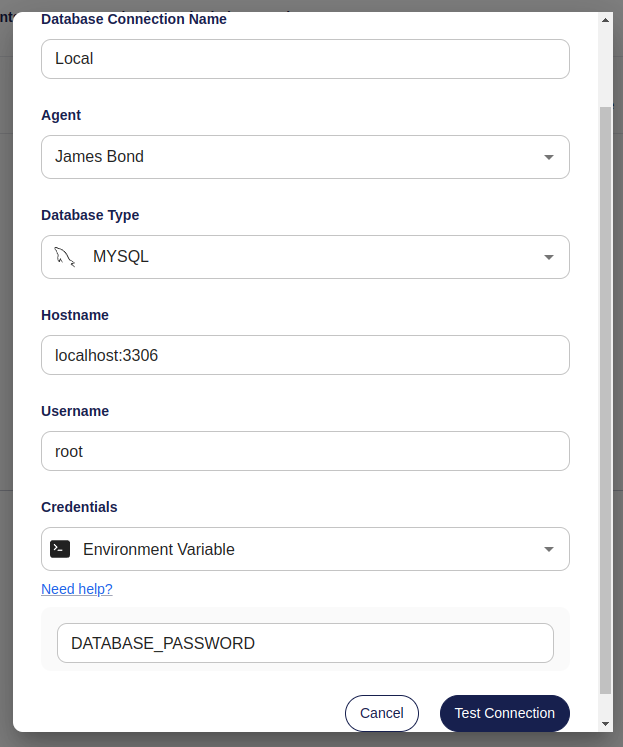
- AWS RDS Token (IAM Auth)
- AWS Secrets Manager
- GCP Cloud SQL Token (IAM Auth)
- GCP Secrets Manager
- Environment Variable
AWS RDS databases offer to obtain a short-lived token using an IAM role to authenticate against an RDS instance.
-
Enable IAM Authentication for your database. For instructions on how to do this, see the AWS documentation.
-
Create an IAM role with the "rds-db:connect" permission for the specific database and user. For instructions on how to do this, see the AWS documentation.
All other info required to obtain a token is derived from the RDS endpoint you define in the connection modal.
AWS Secrets Manager is a secret store you can use to retrieve a secret from. This is somewhat similar to IAM
authentication, since in this case you need to have access to the secret's store, usually using IAM authentication.
Find the secret name and region for your secret. If you need more info,
read this guide. If your secret is stored as JSON, e.g. when you
choose to let RDS handle your database password in the Secrets Manager, you can provide the path to the actual token
using a dot-notation. For example, for a secret like {"password":"my_passw0rd!"} you'd provide .password as the path
to the token.
GCP CloudSQL offers using IAM Authentication to generate a short-lived token to use for authentication against a GCP CloudSQL database.
-
Enable IAM Authentication for your database. For instructions on how to do this, see the GCP documentation.
-
Create a database user and grant it permission to authenticate using IAM, see the GCP documentation for instructions.
All other info required to obtain a token is derived from the CloudSQL endpoint you define in the connection modal.
GCP Secrets Manager is a secret store you can use to retrieve a secret from. Find the project ID and secret name of your
secret. If you need more info, read this guide. If your secret is
stored as a JSON, you can provide the path to the actual token using a dot-notation. For example, for a secret like
{"password":"my_passw0rd!"} you'd provide .password as the path to the token.
You can tell the Agent to look for the password in an environment variable. For example, if your password lives in an
environment variable like DATABASE_PASSWORD=passw0rd you'd provide DATABASE_PASSWORD to the Agent.
We advise to use either IAM authentication or a Secrets Manager to obtain a database password.
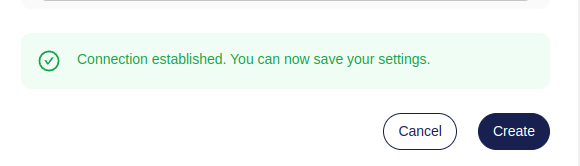
To ensure the credentials are correct, Atlas will check if the credentials are working before we can save them. Hit the Test Connection button and wait. It can take a few seconds before the Agent will pick up the job and check the connection to the database.
If all goes well, we should see a message telling us that Atlas was able to connect to our database through the Agent.
Screenshot Example
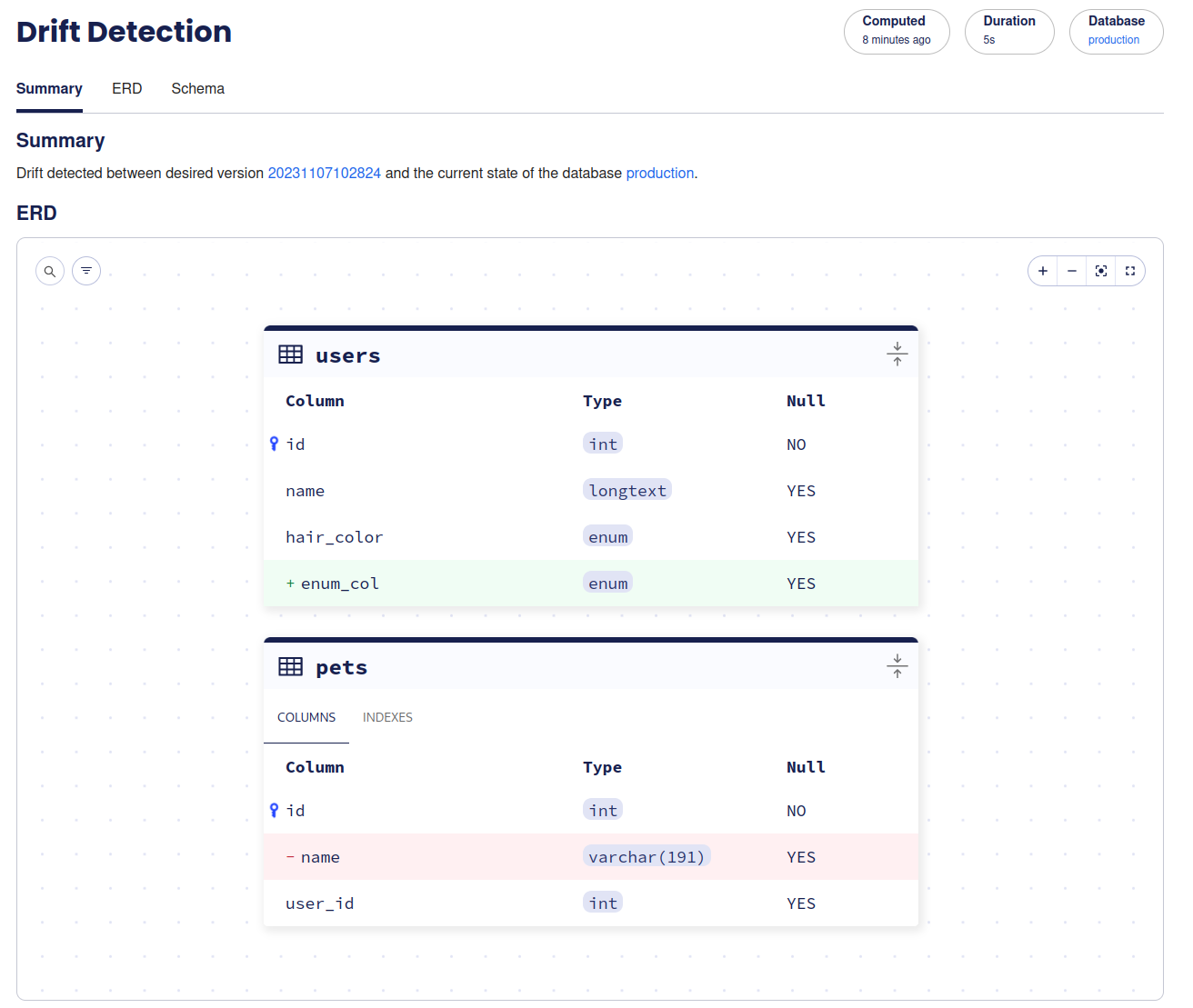
Drift Detection
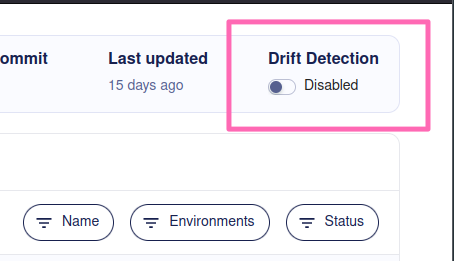
Once Atlas can connect to your database, it can start monitoring your schema and warn you if it detects a drift between your migration directory and its deployment. In the migration directory overview, click on Enable Drift Detection. You'll be asked which database connection the deployments are reachable on.
Screenshot Example
Once enabled, Atlas will run drift detection jobs twice a day. If there is a drift, Atlas will provide you with detailed information about the drift, including an ERD, HCL diff and SQL statements required to fix the drift.
Do not apply the SQL blindly to fix the drift. It is potentially destructive.
Screenshot Example
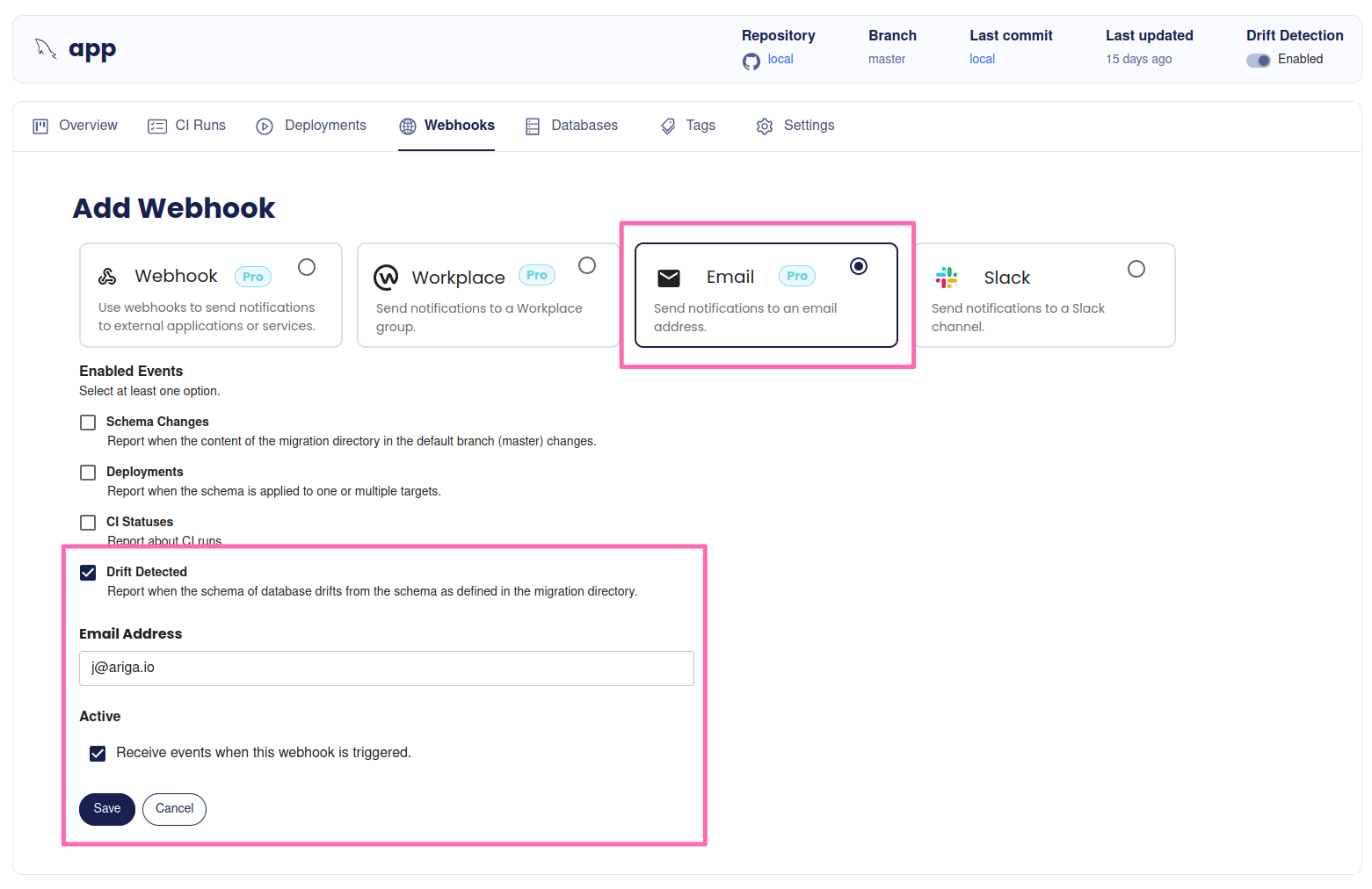
Notifications
You can instruct Atlas to notify you if there is a drift. Atlas supports various channels, such as email, Slack, Workplace or by a plain webhook.
Screenshot Example