Atlas v0.38: Linting Analyzers, PII Detection, Migration Hooks, and More
Hi everyone!
We're excited to share with you the release of Atlas v0.38, filled with many new features and enhancements for you to try.
- Oracle Triggers and Views - We've expanded the support for Oracle schemas to include triggers and views.
- Snowflake Additions - Our library of supported resources for Snowflake has also expanded with the additions of stages, external tables, hybrid tables, and dynamic tables.
- Google Spanner Additions - Spanner users can now manage geo-partitioning placements, locality groups, sequences, and change streams with Atlas.
- Expanded Analyzer Detection - Our linting analyzers now detect SQL injections in SQL schema and migration files, and incorrect usage of transactions in migration files.
- HTTP Data Source - Users can now use HTTP endpoints as data sources in the Atlas configuration file.
- PII Detection - Objects containing potentially sensitive or PII data can now be automatically or manually tagged in the Atlas Registry.
- Pre/Post-migration Hooks - Pre- and post-migration hooks enable teams to run custom logic before and after applying migrations.
- Atlas Monitoring - The Atlas Agent can now automatically discover and monitor RDS instances across multiple AWS accounts using IAM role assumption.
- Azure DevOps Repos CI/CD Integration - Atlas now provides native integration with Azure DevOps Pipelines and Azure Repos, including a dedicated Azure DevOps extension for seamless database schema CI/CD workflows.
We're eager to share that our beta drivers are growing to support more features to better manage schemas across database types.
- macOS + Linux
- Docker
- Windows
To download and install the custom release of the Atlas CLI, simply run the following in your terminal:
curl -sSf https://atlasgo.sh | ATLAS_FLAVOR="oracle" sh
To pull the Atlas image and run it as a Docker container:
docker pull arigaio/atlas:latest-extended
docker run --rm arigaio/atlas:latest-extended --help
If the container needs access to the host network or a local directory, use the --net=host flag and mount the desired
directory:
docker run --rm --net=host \
-v $(pwd)/migrations:/migrations \
arigaio/atlas:latest-extended migrate apply \
--url "oracle://PDBADMIN:Pssw0rd0995@localhost:1521/FREEPDB1"
Download the custom release and move the atlas binary to a file location on your system PATH.
Oracle Support Additions
With Atlas v0.38, we have expanded our Oracle driver (currently in beta) to include support for triggers and views in your schema management. This means that any triggers and views in your Oracle schemas will be included in automatic schema inspections, schema diffs, etc.
-- [...schema truncated for space]
-- Trigger that records any salary change
CREATE TRIGGER TRG_UPDATE_SALARY_AUDIT
AFTER UPDATE OF SALARY ON EMPLOYEES
FOR EACH ROW
WHEN (OLD.SALARY != NEW.SALARY)
BEGIN
INSERT INTO SALARY_AUDIT (EMP_ID, OLD_SALARY, NEW_SALARY, CHANGE_DATE)
VALUES (:OLD.EMP_ID, :OLD.SALARY, :NEW.SALARY, SYSDATE);
END;
-- View that shows employees with department names and computed annual salary
CREATE VIEW EMPLOYEE_INFO_VIEW AS
SELECT
e.EMP_ID,
e.FIRST_NAME || ' ' || e.LAST_NAME AS FULL_NAME,
d.DEPT_NAME,
e.SALARY,
(e.SALARY * 12) AS ANNUAL_SALARY,
e.HIRE_DATE
FROM EMPLOYEES e
JOIN DEPARTMENTS d ON e.DEPT_ID = d.DEPT_ID;
Snowflake Support Additions
Atlas v0.38 introduces broader support for our Snowflake driver (currently in beta), providing more flexibility in using Atlas to manage your Snowflake schema.
Newly supported resources include:
-
Stages: Define external storage locations for loading and unloading data.
schema.hclstage "mystage" {
schema = schema.public
url = "s3://mybucket/data/"
storage_integration = "my_integration"
directory_enabled = true
comment = "This is my stage"
} -
External Tables: Refer to data stored outside Snowflake, such as in S3, and query it as if it were a regular table.
schema.hclexternal_table "events" {
schema = schema.public
column "event_id" {
type = VARCHAR(255)
as {
expr = "value:c1::varchar"
}
}
location {
stage = stage.mystage
path = "data/events/"
}
} -
Hybrid Tables: Combine transactional and analytical workloads in a single table, supporting flexible data operations.
schema.hclhybrid_table "users" {
schema = schema.public
column "id" {
comment = "User ID"
type = VARCHAR(255)
}
primary_key {
columns = ["id"]
}
...
} -
Dynamic Tables: Define tables that automatically refresh based on upstream changes, supporting incremental or full refresh modes.
schema.hcldynamic_table "users" {
schema = schema.public
column "id" {
comment = "User ID"
}
target_lag = DOWNSTREAM // or "<num> { seconds | minutes | hours | days }"
refresh_mode = INCREMENTAL, or FULL
as = "SELECT * FROM users"
...
}
Read more about implementing these resources in the Atlas configuration documentation.
Google Spanner Support Additions
Atlas v0.38 also comes with more support for the Google Spanner driver (currently in beta) to improve managing your Spanner schema with Atlas.
The newly added resource support includes:
-
Geo-partitioning Placements: Partition logical tables at the row level into distinct placements mapped to different instance partitions to serve data locally by region while maintaining one unified database.
schema.hcltable "Orders" {
schema = schema.default
column "Location" {
null = false
type = STRING(MAX)
placment_key = true
}
primary_key {
columns = [column.OrderId]
}
}
placement "europeplacement" {
instance_partition = "euro-partition"
default_leader = "europe-west1"
} -
Locality Groups: Control whether their data uses high-performance SSD storage, standard HDD storage, or flexible age-based policies that transition data from SSD to HDD over time.
schema.hcltable "t1" {
schema = schema.default
locality_group = locality.hotspot_group
}
locality "hotspot_group" {
storage = "ssd"
ssd_to_hdd_spill_timespan = "24h"
} -
Sequences: Generate a series of unique integer values to use as a column's default value (e.g., ID numbers).
schema.hcltable "Orders" {
schema = schema.default
column "OrderId" {
null = false
type = INT64
default = sql("GET_NEXT_SEQUENCE_VALUE(SEQUENCE orders_sequence)")
}
primary_key {
columns = [column.OrderId]
}
}
sequence "orders_sequence" {
kind = bit_reversed_positive
} -
Change Streams: Capture and stream data changes (e.g., inserts, updates, and deletes) from a database in near real-time.
schema.hclstream "OrdersStream" {
tables = [table.Orders]
options = {
retention_period = "7d"
value_capture_type = "NEW_ROW"
}
}
Read more about using Atlas's Google Spanner driver in our guides and docs.
Expanded Analyzer Detection
Atlas contains a number of analyzers and checkers that automatically detect destructive changes, backward-incompatible changes, and much more. These have been expanded to include flagging nested transactions and detecting SQL injections that can make schemas or migrations vulnerable to untrusted input.
Transactions in Migration Files
Atlas wraps all migration files in individual transactions by default, which can cause errors when manually-written migration
files contain their own transaction statements (for example, START TRANSACTION).
The nestedtx analyzer flags these statements, allowing you to handle the overlap by either removing the manual transaction
control or adding -- atlas:txmode none to the file header to indicate that this migration file should not be wrapped in a
transaction by Atlas.
SQL Injection Analyzer
The SQL injection analyzer scans migration files and declarative schemas for potentially vulnerable SQL constructs. It detects unsafe dynamic SQL patterns like string concatenation and variable interpolation that could allow untrusted input to be executed.
With the increasing use of automated tools and AI assistance in schema development, this analyzer helps catch unintentional security risks early in the development cycle with two checks:
- Use of
EXEC/EXECUTEstatements with string concatenation or variable interpolation - Dynamic SQL construction using improper string operations
This analyzer is currently only supported on the PostgreSQL driver, with plans to expand to MySQL and SQL Server in the next release.
Example output
Analyzing changes from version 1 to 2 (1 migration in total):
-- analyzing version 2
-- possible SQL injection vulnerabilities detected:
-- L11: expression concatenates parameter(s) into dynamic statement
https://atlasgo.io/lint/analyzers#SA101
-- L25: function call propagates parameter into dynamic statement without sanitization
https://atlasgo.io/lint/analyzers#SA101
-- ok (234.583µs)
-------------------------
-- 500.5µs
-- 1 version with warnings
-- 11 schema change'
-- 6 diagnostics'
HTTP Data Source
Atlas now supports using an HTTP endpoint as a data source, allowing you to fetch
data from internal and external services and use it dynamically in your project configuration. It can perform GET, HEAD,
or POST requests, with the option to include headers, a request body, timeouts, TLS certificates, and retry logic.
After the request runs, Atlas exposes attributes like the response body, headers, status code, and URL, which can be referenced in your configuration (e.g., pulling a secret or setting an environment variable based on an API response).
Example
data "http" "example" {
url = "https://service.example.com/search?q=atlas"
method = "GET"
request_headers = {
"Accept" = "application/json"
}
request_timeout_ms = 5000
retry {
attempts = 2
min_delay_ms = 100
max_delay_ms = 1000
}
}
env "dev" {
src = "file://schema.my.hcl"
url = "mysql://root:${urlescape(jsondecode(data.http.example.response_body).password)}@host:3306/database"
}
PII Visibility and Detection
Atlas Registry now supports tagging database objects that contain potentially sensitive or personally identifiable information (PII). This capability helps organizations meet privacy, security, and compliance requirements such as SOC 2, GDPR, and ISO 27001, which require visibility and control over how personal data is stored and accessed.
Atlas automatically detects objects that may contain PII by using pattern-based analysis of schema metadata to inspect object names, column names, and comments to identify fields likely to store sensitive information. Users can also manually add or remove PII tags (or any other tags, such as "PHI"), filter to view only tagged objects, and maintain a consistent data classification strategy across environments.
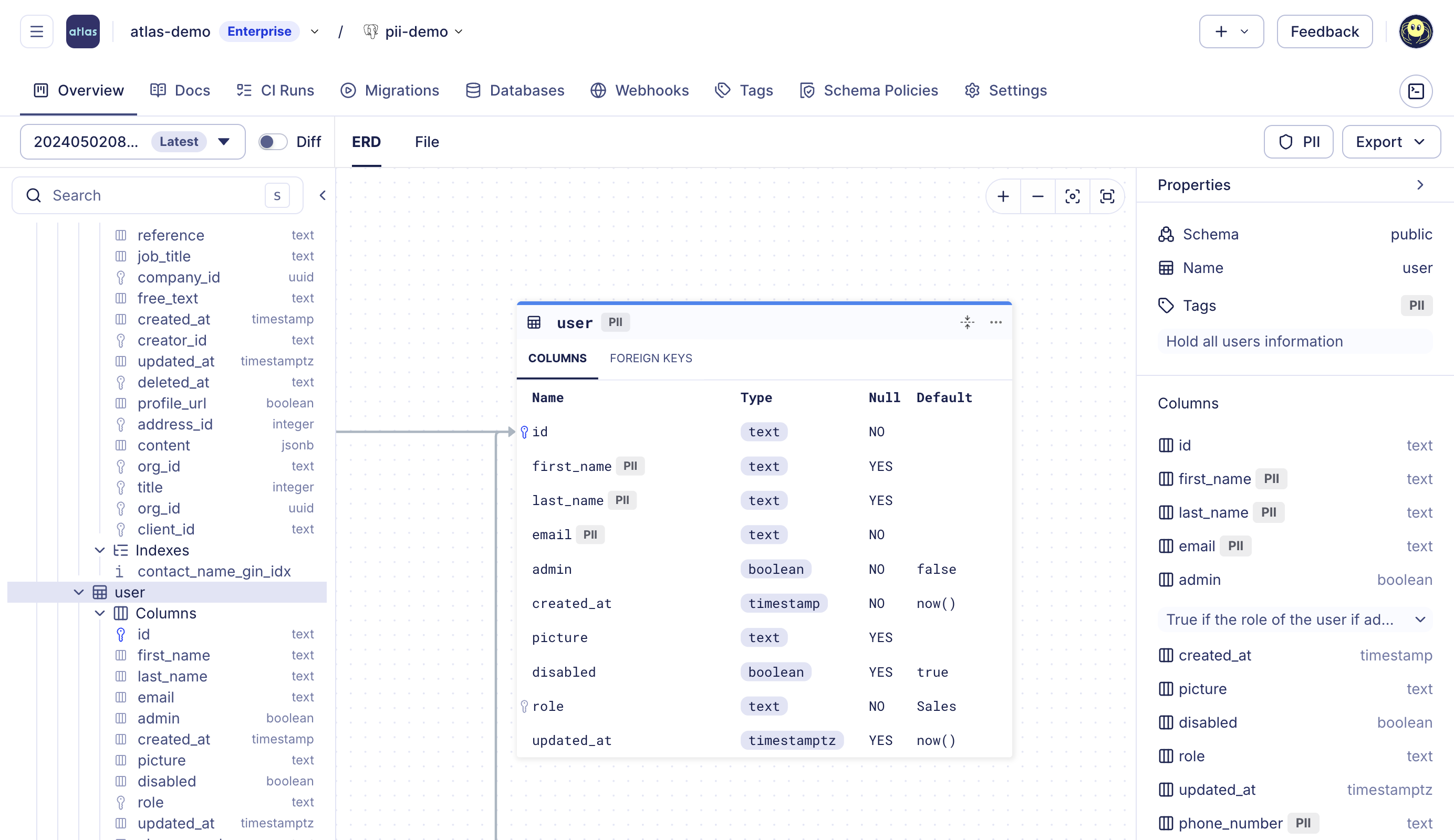
PII tagging in Atlas Registry
Pre- and Post-migration Hooks
Pre- and post-migration scripts are now generally available. They let teams run custom logic before and after applying migrations. This is ideal for enforcing guardrails, refreshing materialized views, or seeding and updating data as part of the migration deployment process.
env {
name = atlas.env
pre "migrate_apply" {
skip {
condition = atlas.env == "staging"
message = "Skipping staging warm-up"
}
exec {
src = "file://scripts/pre-flight.sql"
}
}
post "migrate_apply" {
exec {
src = "file://scripts/analytics_refresh.sql"
on_error = BREAK
}
}
}
Example output
Executing pre-migration hooks (1 hook in total):
-- hook 1/1 at atlas.hcl:11 (2 statements):
-> CALL ensure_guardrails();
-> CALL validate_data_integrity();
-- ok (4.583µs)
-------------------------------------------
Migrating to version 1 (1 migrations in total):
-- migrating version 1
-> CREATE TABLE t1(c1 int);
-> ALTER TABLE t1 ADD COLUMN c2 int;
-- ok (148.583µs)
-------------------------
-- 911.5µs
-- 1 migration
-- 2 sql statements
-------------------------------------------
Executing post-migration hooks (1 hook in total):
-- hook 1/1 at atlas.hcl:23 (2 statements):
-> REFRESH MATERIALIZED VIEW CONCURRENTLY analytics.latest_activity;
-> CALL sync_reporting_cache();
-- ok (4.375µs)
Hooks run outside the migration transaction and can be conditionally skipped with skip { condition = ... }.
This feature provides fine-grained control and automation around database change execution.
Atlas Schema Monitoring
In the previous release, we added the ability to automatically discover database instances for monitoring using the Atlas Agent, rather than manually creating them in the Atlas Cloud.
Expanding on this feature, we have now added the ability to discover and monitor RDS instances across multiple AWS (sub-)accounts by assuming an IAM role if a trusted relationship is established. Read more about this in our docs.
Azure DevOps Repos CI/CD Integration
Atlas now provides first-class support for Azure DevOps, bringing professional database CI/CD workflows to teams using Azure Repos and Azure Pipelines. This integration includes a dedicated Azure DevOps extension that simplifies the setup and execution of schema migration workflows.
Getting Started with Azure DevOps
Setting up Atlas with Azure DevOps takes just a few steps. Here's a quick example of what the pipeline configuration looks like:
View configuration
trigger:
branches:
include:
- main
paths:
include:
- 'migrations/*'
- 'azure-pipelines.yml'
pr:
branches:
include:
- main
paths:
include:
- 'migrations/*'
pool:
vmImage: ubuntu-latest
variables:
- group: atlas-vars
steps:
- checkout: self
persistCredentials: true
fetchDepth: 0
fetchTags: true
- script: |
echo "Configuring git user for commits...."
git config user.email "azure-pipelines[bot]@users.noreply.github.com"
git config user.name "azure-pipelines[bot]"
displayName: 'Configure Git User for Commits'
- script: curl -sSf https://atlasgo.sh | sh
displayName: Install Atlas
- script: atlas version
displayName: Atlas Version
- script: atlas login --token $(ATLAS_TOKEN)
displayName: Atlas Login
# Lint migrations on pull requests
- task: AtlasAction@1
condition: eq(variables['Build.Reason'], 'PullRequest')
env:
SYSTEM_ACCESSTOKEN: $(System.AccessToken)
inputs:
action: 'migrate lint'
dir: 'file://migrations'
dir_name: 'app-schema-2'
config: 'file://atlas.hcl'
env: 'ci'
displayName: Lint Migrations
# Push migrations to Atlas Cloud on main branch
- task: AtlasAction@1
condition: and(succeeded(), eq(variables['Build.SourceBranch'], 'refs/heads/main'))
inputs:
action: 'migrate push'
dir: 'file://migrations'
dir_name: 'app-schema-2'
latest: true
env: 'ci'
displayName: Push Migrations
# Apply migrations to database on main branch
- task: AtlasAction@1
condition: and(succeeded(), eq(variables['Build.SourceBranch'], 'refs/heads/main'))
inputs:
action: 'migrate apply'
dir: 'file://migrations'
url: $(DB_URL)
displayName: Apply Migrations
This pipeline automatically:
- Lints new migrations when you open a pull request, surfacing potential issues directly in your PR,
- Pushes migration directories to Atlas Cloud's Schema Registry when changes merge to main, and
- Applies pending migrations to your target database with the connection string from your pipeline variables.
For more information on how to set up Atlas with Azure DevOps, see the Azure DevOps Repos CI/CD Integration guide.
Change in v0.38: atlas migrate lint
As announced in v0.37, starting with v0.38, the, the atlas migrate lint command will no longer be included in
the Starter (free) plan of Atlas.
The code remains open-source (Apache 2 license) and available in Atlas Community Edition. If you need the command without
using Atlas Pro, you can still build Atlas from source or use the community binary.
We want to be transparent about this change. Over time, migrate lint was split between the Starter and Pro plans,
creating extra maintenance overhead. At the same time, the shift toward AI-driven schema changes highlights the need for
stronger, deterministic guardrails. To focus on that, we're keeping the existing lint engine in the Community build while
rewriting the new engine with advanced checks and governance features, included in the official binary and available only
in Atlas Pro.
This reduces complexity in the official binary and lets us focus on advancing Atlas in the areas teams and AI systems rely on most. Users of the free version can still run linting through Atlas Community, while Pro users remain unaffected.
Wrapping Up
Atlas v0.38 adds support for additional database-specific features and introduces several security and workflow improvements.
This release expands database platform coverage with Oracle triggers and views, Google Spanner geo-partitioning placements and locality groups, and stages, external tables, hybrid tables, and dynamic tables for Snowflake.
New security analyzers detect SQL injection patterns and transaction issues in migration files. HTTP data sources allow dynamic configuration from external APIs, while PII detection helps with data governance.
Additional features include pre- and post-migration hooks, schema monitoring capabilities, and Azure DevOps integration with a marketplace extension.
We hope you enjoy these new features and improvements. As always, we would love to hear your feedback and suggestions on our Discord server.
